Basics of thread
Threads varies in many ways. In the following we explain the basics of thread. You can also check out our FAQ section for thread.
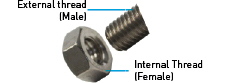
Gender
Every matched pair of threads, external and internal, can be described as male and female. For example, a screw has male thread, while the matching hole has female thread.
Handedness
The helix of a thread twists in one of two possible directions. Most threads are oriented so that the threaded item when seen from a point of view on the axis through the center of the helix, moves away from the viewer when it is turned in a clockwise direction and moves towards the viewer when it is turned counter-clockwise.
By convention right-handedness is the default handedness for screw threads. Most threaded parts and fasteners therefore have right-handed threads.

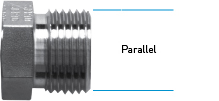
Design
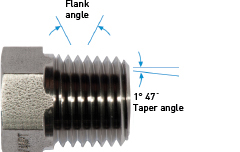
The type of thread can be identified by the following characteristics: parallel and tapered design (see images right).

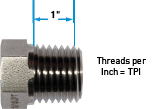
Pitch/TPI
The pitch is the distance from the crest of one thread to the next in milimeters (mm).
TPI (threads per inch) is used by inch thread.
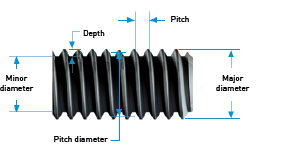
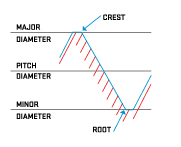
Diameter
The major diameter is determined by the thread tips.
The minor diameter is determined by the groove of the thread.
The pitch diameter is the distance between the tips of two opposite flanks or the length of the centreline of the profile.
Angle
The flank angle is the angle between the flank of a screw thread and the perpendicular line to the axis of the screw. Tapered threads have a taper angle. This is the angle between the taper and the center axis of the pipe.
Crest / root
The outermost part of the thread is called 'crest', the innermost part of the thread is called 'root'.
Dimensions of thread types
M - Iso thread (Metric)
View the table
M Coarse Thread ISO 724 (DIN 13-1)
M Fine Thread ISO 724 (DIN 13-2 to 11)
NPT - Pipe thread
View the table
NPT ANSI B1.20.1
NPTF ANSI B1.20.3
G/R/RP - Whitworth thread (BSPP/BSPT)
View the table
G = BSPP ISO 228 (DIN 259)
R/Rp/Rc = BSPT ISO 7 (DIN 2999 replaced by EN10226)
UNC/UNF - Unified national thread
View the table
UNC ANSI B1.1
UNF ASNI B1.1
Download the types of thread document

Download!
Please login to download the Types of thread document!
No account yet? Click here to create a new account!
Basics of thread
- Gender
- Handedness
- Design
- Pitch / TPI
- Diameter
- Angle
- Crest / root
Most common threads
- M - ISO thread (metric)
- NPT - Pipe thread
- G/R/Rp - Whitworth thread (BSPP/BSPT)
- UNC/UNF - Unified National thread
- Extra: Comparison sheet (M - BSPP - BSPT - NPT - UNC - UNF)
Thread Seal Types
- Conversion factor
- Other threads
Frequently asked questions
- How to identify thread types?
- What does NPTF stand for: Female, fine or fuel?
- Which female threads are tapered/conical?
- What is the difference between G-thread (BSPP) and R-thread (BSPT)?
- Can I use an o-ring sealing with NPT thread?
- Are NPT and BSP Pipe threads compatible?
- What is screw/nut galling and how can it be avoided?
- What kind of sealing method is recommended when mounting a PA/PVDF fitting with male tapered thread into a metal counterpart?
- What kind of thread does a JIC-fitting have?
Any Questions?
More information about our products, services or looking for a custom solution?
Please contact our Sales Engineers.

WE MAKE YOUR TECHNOLOGY WORK
NL - Tel. +31 70 413 07 50
USA - Tel. +(1) 973 383 0691
CN - Tel. +86 (10) 56865822/56865835
TW - Tel. +886-(0)3-5600560